Nanotechnology for Environmental Remediation
Nanotechnology is the science where molecules and particles within the nanometer range are studied.
This field of science is extremely diverse and often quite complex. Nanotechnology is used in fields such as Energy, Biomedical Science, Agriculture, Construction Sector, Engineering Science and Environmental Science.
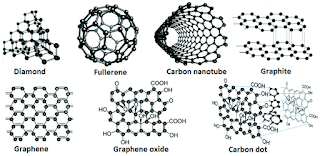
Different types of Carbon nanomaterials
Environmental pollution remains the world’s greatest problem facing humanity and the leading environmental cause of morbidity and mortality. Man’s activities through urbanization, industrialization, mining, and exploration are at the forefront of global environmental pollution.
Environmental remediation is defined as removing contaminants from the environment. Environmental remediation encompasses all the remediation methods employed to reduce the risks of environmental pollution. Nanotechnology could be very useful in reducing existing environmental problems.
New novel nanomaterials developed based on several techniques have further increased the threat to the environment and as a result human health. Hence, the synthesis of nanomaterials-based eco-friendly methods become important and therefore attracted the attention of the scientific community.
This review explores the different types of nanoparticles, available today for remediation purposes
1.) Iron Nano Particles
These particles are widely used in wastewater treatment projects. And also they are used to deconstruct waterbodies and soils which has been contaminated by herbicides like Atrazine.
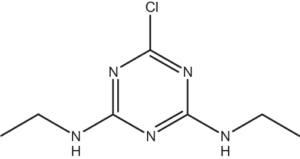
Molecular structure of Atrazine
Advantages of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Iron oxide nanoparticles have attracted much consideration due to their unique properties, such as,
- Super-para-magnetism
- Surface-to-volume ratio
- Greater surface area
- Easy separation methodology
Under this scenario, there is a need to predict the environmental effect of these nanoparticles in the near future. Additional disadvantages include economic disruption and possible threats to security, privacy, health, and the environment.
2.) Semiconductor Nano Particles
These nanoparticles are commonly used in environmental remediation.
For an instance, Titanium dioxide (TiO2) has been considered a useful material for the treatment of wastewater due to its non-toxic character, chemical stability, and excellent electrical and optical properties which contribute to its wide range of applications, particularly in environmental remediation technology.
3.) Bioremediation
Bioremediation is a process whereby engineers use something living, like a microorganism, fungus, or green plant, to return a polluted environment back to its original state.
Some examples of bioremediation-related technologies :
1. Phytoremediation
2. Bioventing
3. Bioattenuation
4. Biosparging
5. Composting (biopiles and windrows)
6. Landfarming.
Other remediation techniques include thermal Desorption, Vitrification, Air stripping, Bioleaching, Rhizofiltration, and Soil Washing.
This method is used to remove harmful organic compounds such as Carbazole (CA) and Dibenzothiophene (DBT)

Magnetite can be used in bioremediation. Bioremediation is eco-friendly, cost-effective, and scalable.
One of the major disadvantages to bioremediation is the limitations on the types of contaminants that it can remove effectively
Although a variety of studies have been undertaken to investigate the use of nanotechnology, concerns regarding the application of nanotechnology for environmental remediation purposes have yet to be addressed. Therefore, research is necessary to implement an environment for remediation using nanotechnology in order to avoid the possibility of these materials becoming a source of environmental contamination.
Article By – Isiri Withanawasam
References
- (PDF) Nanotechnology for Environmental Remediation: Materials and Applications (researchgate.net)
- Environmental remediation – Wikipedia
- Advantages and Disadvantages of using nanoparticles – Mrs Joyce (google.com)
